|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| LAYMAN’S REPORT ON LIFE 99/ENV/GR/000557 PROJECT LIFE 99/ENV/GR/000557 project, entitled “LIFE-Thyamis: Actions for the integrated management in the catchments areas and estuaries of two rivers”- The case of Kalamas (Greece) and Lynher (United Kingdom), was developed in the districts of NW Greece (Epirus) and SW England (Cornwall) and lasted 2 and ½ year (1/11/1999 - 30/4/2002). The project’s overall budget was 796.774,46 € whereas EC’s financial contribution was 371.907,92 €. Project’s target was to apply actions and develop tools for the integrated management and sustainable development in the catchments areas and estuaries of rivers Kalamas and Lynher. Main problems regarding Kalamas’ basin management focus on agricultural and animal farming polluting activities. Urban and industrial wastes contribute also to the river’s pollution. All pressures exerted against the river are so far poorly faced due to the lack of a management and coordination plan between the relevant official administrations and agencies as well as of a monitoring system for the sufficient surveillance on the river’s water quality. Main problem regarding Lynher’s basin management is water quality due to pollution and soil erosion, both related to the agricultural activities in the area. Aims and expected results of the project were:
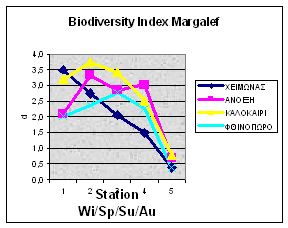
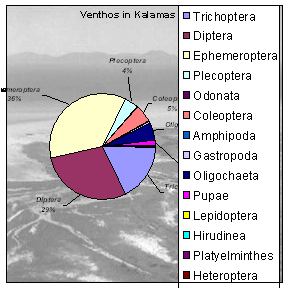
Related and complementary to each other actions construct the project, since no similar actions for environmental awareness and protection have ever so far been applied in Kalamas area, while in Lynher’s area, a significant infrastructure existed due to other projects run in the past and therefore the English partners focused on a few specific complementary actions and the know-how transfer to the Region of Epirus. Actions, methods and the results of the project are described below: Action 1 “Description of the existing situation” aimed to spatial registration and framing of the existing status in order to proceed effectively to the integrated environmental management and sustainable development. Prefecture of Ioannina elaborated a study entitled ”Description of the existing situation – imprinting of Kalamas basin evolution” and Prefecture of Thesprotia a study entitled ”Description of the existing situation – recording the environmental evolution of Kalamas basin in Thesprotia”. The drawing up of the- foreseen in action 9- management plan was based on the above studies. Action 2 “Development of GIS in Kalamas River” targeted the creation of an environmental database and the development of tools for the effective management and incorporation of environmental information into Kalamas basin and estuaries land-planning. Prefecture of Epirus has developed a GIS, for the integrated management of The following actions were proclaimed: - Digitization of land uses, hydrographic network, existing human activities, ecosystems, archaeological sites, historic landscapes and environmental infrastructure. - Applications such as: land- use changes, incorporation of the river’s simulation model (action 4), and input of monitoring data. Recorded by the automatic stations (action 3). Action 3 “Monitoring program” included: a. sampling over a year and evaluation of the appropriate physicochemical and biological parameters for the identification of river’s stress factors and b. installation of three automatic monitoring stations across Kalamas river in order to follow up critical, according to Action 3 –a, stress factors. All data will be introduced to GIS for use either to the simulation model or the management plan. The University of Ioannina analyzed water and sediment samples collected, from six chosen sites along the river, twice every month, during January to December 2000 for over thirty physicochemical parameters. Conclusions, in brief, according to results are: Kalamas River: 1. Is subjected to seasonal pesticide pollution 2. Has suffered long term metal pollution, especially by nickel (Ni), according to sediment analysis. 3. Indicates, according to BOD5, DO, nutrients and biological indicators (benthos) analysis, a rather healthy river ecosystem, excluding the estuaries area. 4. Holds exceptional esthetic characteristics. According to EC Directive on Surface Water Abstraction (75/440/EEC) (and the American Εnvironmental Protection Agency-EPA) Thyamis may be listed as Class 1B-good quality borderline to Class 2-fair, in reference to General Quality Assessment-GQA, a classification evaluating both chemical and biological characteristics. The TEI of Epirus performed chlorophyll-a concentrations and benthos analysis during the same period. Conclusions are: Kalamas River, 1.Responds to satisfactory quality criteria, in reference to biological indicators, at most sampling sites and time periods. Low lands though near estuaries, downgrade water quality producing eutrophic trends and disappearance of species regarded as quality indicators. 2.Hydrological conditions (water supply, flow velocity) play a determining role in water quality whereas human activities (dams, building material delivery or discharge) modify ecosystems’ diversity affecting the presence and survival of aquatic organisms. 3.Despite the presence of polluting factors (farming and urban waste etc) is characterized by the considerably limited eutrophism evident only at unfavorable hydrological conditions (reduced flow velocity, high temperatures). Following the evaluation of the results, Region of Epirus, according to legislation, proceeded to the implementation of three monitoring stations for the following parameters recording: DO, T, S, pH, ORP, TTS, depth, conductivity, turbidity, special gravity while one of the stations will also monitor NO3, NO2, N, Ca.
A math model is the solution to a system of equations simulating the natural river processes where the various factors affecting these processes are the variables. Prediction and control over these factors (dissolved oxygen, biological oxygen demand, temperature etc) offers prognosis and avoidance of unfavorable for the ecosystem consequences. Prediction also offers time to investigate alternative scenarios for better choices in reference to integrative management of water resources QUAL2E, simulation model, developed by the Environmental Protection Agency - Action 5 “Reintroduction and protection of Kalamas fish species” is linked to the progressive reinforcement of Salmo truta populations and the reintroduction of Acipencer naccari, an eliminated and nowadays under protection species. Salmo truta population reinforcement included genitors arrest, reproduction and enrichment of the river with 25.000.000 fish fries, whereas 1.500 Acipencer naccari offspring of genitors purchased from A significant number of Acipencer individuals survived although better results would have been achieved if reintroduction had been attempted with better seized genitors and at more appropriate river zones. Salmo truta’s survival ratio was high and population recovery may be predicted very effective if protective measures (especially against illegal fishing) and reasonable enrichments would be established. Action 6 “Environmental indicators” concerned the selection of the appropriate indicators for sustainable development as another tool for the river’s management. Indicators were embodied in the GIS and will contribute to better info use. Action 7 concerned the establishment of a co-ordination council and two local observatories, targeting the promotion of cooperation between involved agencies. A temporary co-ordination council was established for the management of Kalamas basin and estuaries until a permanent Management Authority will be founded. The KEPPEs (Environmental Control Committees) of both Prefectures (Ioannina and Thesprotia) were engaged as the local observatories, responsible for the monitoring stations and the observance of the environmental terms. The two observatories will also be in contact with the Coordination council in order to prepare seminars or open discussions, in the rural areas, regarding environmentally friendly techniques and rational use of fertilizers, pesticides and irrigative water. Action 8 “Raise of farmer’s awareness on environmentally friendly techniques” aimed to, due to rural activities, pollution’s reduction, by promoting environmentally friendly techniques. Therefore seminars were held, pamphlets and guides were published and expert visits in farms took place. Action 9 “Management Plan” targeting to an integrated management plan of Kalamas basin, based on the existing situation (action 1), the know-how on management issues transferred by our English partners.(action 13) and the hierarchy of targets by the co-ordination council (action 7) was constructed by the Region of Epirus Action 10 “Classification of historic landscape at Lynher catchments area” Cornwall’s landscape was mapped and described by means of a certain number of categories and types of local historic characteristics. Next, a classification – mapping was performed via a method developed by the Archaeological Department of Cornwall County and planned to cover the needs of all future users. This action, additionally, gave the opportunity for the method’s demonstration at national as well as at European level. Action 11 “Incorporation of new applications and data into Cornwall’s GIS” concerned the development of management tools contributing the long-term observance of management practice efficiency over the river basin. New elements, found by the methodology described in action 10, were incorporated into the GIS developed during 1994-97 Life project. Action 12 “Documentation, advisory support and motivation for the farmers in Lynher” included updating and information networks, visits of experts and financial offers and benefits for the adaptation of environmentally friendly practices. Action 13 “Interregional cooperation” targeted a. the transfer of know how on integrated management of coastal areas and river estuaries and b. the demonstration and appliance in the Region of Epirus of specialized methods and techniques developed in Cornwall County. This action included farmers’ exchange and workshops between the two Regions, where the GIS system developed in Cornwall and the classification of historic landscapes mentioned in action 10,were demonstrated. Awareness and updating on environmental issues for the local population and agencies are considered essential for project’s success, therefore particular dissemination actions were engaged such as technical reports, workshops, issues and distribution of leaflets and guides, press conferences and reports, presentations and participation to national and international scientific conferences as well as the creation of a web-site in Greek and English language. In conclusion, the methodology on water quality control and assessment of the existing situation as well as the proposed management tools (GIS, sim. model, indicators) may be applied to all similar ecosystems. Furthermore the management proposals are in agreement to the new European and National environmental legislation seeking for: management of aquatic ecosystems as integrated environmental entities in reference to their catchments area, local society participation and corresponding administrative authorities establishment. Finally, the overall impact, of the Thyamis-LIFE project, on the environment is remarkably positive since the project resulted at sustainable and effective protection through the on line connected stations along the river, integrated management of the catchment area with the help of the established official observatories, interregional cooperation on environmental issues between two european countries, dissemination of knowledge on ecosystem's concept and environmental attitudes for the inhabitants of the involved areas as well as perspectives for a more extend similar network over the river ecosystems in the Prefecture of Epirus.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




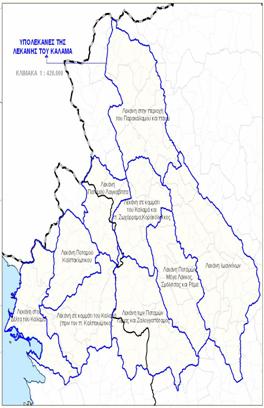 Subbasins of Kalamas
Subbasins of Kalamas 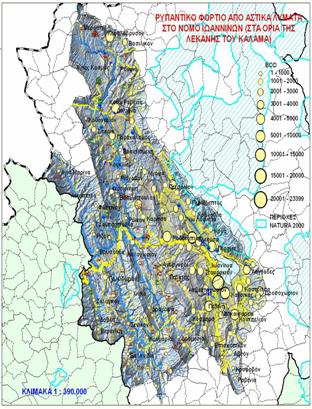 Pollute levels coming from civil waste in Kalamas,
Pollute levels coming from civil waste in Kalamas,  Municipal waste pollution burden in Ioannina
Municipal waste pollution burden in Ioannina Kalamas catchment's secondary basins
Kalamas catchment's secondary basins Kalamas
in ‘Thiogefiro', Prefecture of Thesprotia
Kalamas
in ‘Thiogefiro', Prefecture of Thesprotia  Kalamas in Vrosina, Prefecture of Ioannina
Kalamas in Vrosina, Prefecture of Ioannina